

In addition to ETFs based on water, there are other waters available to the body. Cell membranes separate the if from the interior of the cell by allowing selective passage of materials. The if transports gas, nutrients, and wastes from capillaries to cells. During 24 hours, plasma transports a wide range of materials including blood cells, proteins (including clotting factors and antibodies), electrolytes, nutrients, gases, and wastes. Plasma contains roughly 20 percent of the ECF. The remaining one-third of the body’s amount of water comes from the ECF. intracellular and extracellular fluid Extracellular Fluid In The Body It consists of two primary components, the fluid portion of the blood (called plasma) as well as the interstitial fluid (if) in which all non-blood cells reside. Fluid-containing intracellular membranes are located in a compartment called intracellular fluid (ICF).Īll bodily tissues are covered with extracellular fluid (ECF). There are different body fluid compartments, which are essentially separate from each other due to some physical barrier. The intracellular fluid (ICF) inside each body cell is the fluid that surrounds it. This also refers to the fluid in blood vessels. The interstitial fluid (if) is an extracellular fluid (ECF), which is fluid between body cells. Compartments Of FluidĪ tiny blood vessel surrounded by several cells is shown in the diagram. The balance between the solutes inside and outside of the cells should be maintained to maintain normal function. Therefore, water will enter and exit cells and tissues depending on how concentrated these solutes and waters are. A semi-permeable membrane allows water to diffuse between regions of higher concentration and regions of lower concentration, by way of an osmotic gradient. In this article we shall discuss Extracellular Fluid in detail.Ī process called osmosis occurs in the body in which water moves between compartments by crossing membranes of semi-permeable cells.
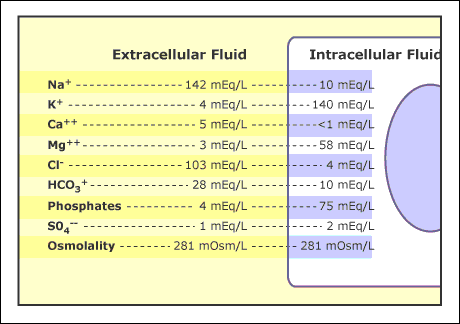
An electrolyte, such as sodium ions (na+) or chloride ions (cl-), may also contain other ions. As used in medicine, an electrolyte is mineral-free from the charge carried by a salt (an ion). A human body consists of a wide variety of solutes, including proteins – the ones that transport lipids, carbohydrates, and, most importantly, electrolytes. In addition to dissolved substances, a solution also contains solutes. As life begins, water solutions play a key role in chemical reactions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
